The International Monetary Fund (IMF) has revised its global growth forecast for 2025, projecting a reduced rate of 2.8%, down from its earlier prediction of 3.3%. This downward revision is primarily driven by the ongoing impact of President Donald Trump’s new tariff measures, which have created significant uncertainty in the global economy. The IMF also lowered its 2026 growth estimate to 3.0%, signaling the extended challenges faced by the global financial landscape.
Rising Trade Tensions and Economic Transformation
IMF Chief Economist Pierre-Olivier Gourinchas, speaking in Washington, emphasized the profound changes the global economy is experiencing. He warned that rising trade tensions, coupled with the uncertainty surrounding tariff policies, could lead to slower growth in the coming years. “We are entering a new era,” Gourinchas stated, underlining the long-term effects of sustained trade disputes.
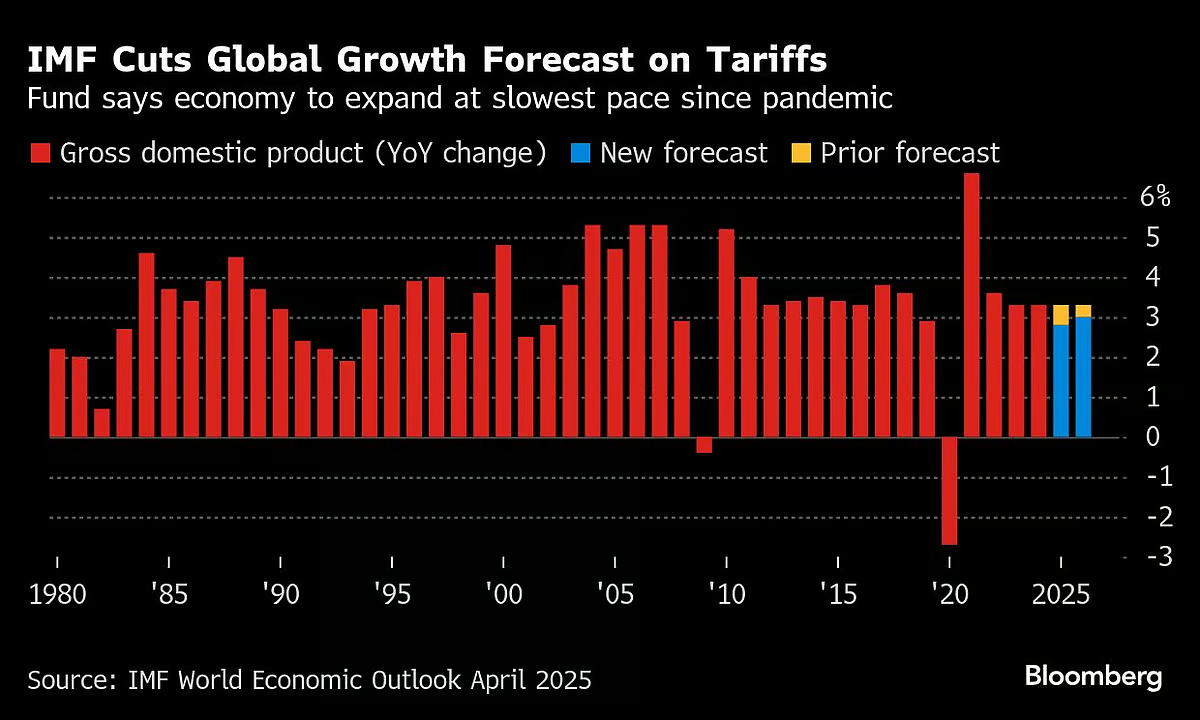
The IMF’s latest forecast reflects the growing strain of trade disruptions, especially following Trump’s tariff hikes. The IMF’s World Economic Outlook included tariff data up until April 4, prior to the most recent increases, some of which have raised tariffs on Chinese imports to as high as 145%.
Impact on US and Global Economies
The IMF has significantly downgraded its US economic growth projection for 2025 to 1.8%, a full 0.9 percentage point reduction from its previous forecast. This adjustment is attributed to factors including heightened trade tensions, policy uncertainty, and weaker demand in key sectors. The IMF now projects US inflation at 3.0% in 2025, decreasing to 2.5% in 2026.
In addition, the IMF’s Global Financial Stability Report warned of increased financial system risks due to tighter financial conditions and the growing uncertainty around trade policies. The unpredictable nature of Trump’s tariff strategy has been flagged as a significant contributor to these financial risks.
Forecast Adjustments for Major Trading Partners
The IMF’s forecast revisions extend beyond the United States, affecting several key global economies. China’s growth outlook has been downgraded to 4.0% for 2025, a decline from the 5.0% growth projected last year. Similarly, Mexico’s economy is expected to contract by 0.3%, while Canada faces a weaker economic outlook. Japan’s growth forecast has also been reduced to a meager 0.6% for both 2025 and 2026.
In Europe, the IMF has lowered its growth projection for the eurozone to 0.8% in 2025. Germany, Europe’s largest economy, is expected to see no growth, while France, the UK, and Italy face downgraded economic outlooks. However, Spain has seen a slight improvement, with its growth forecast raised to 2.5%.
Impact on the Middle East and Sub-Saharan Africa
The IMF has also revised growth projections for the Middle East and sub-Saharan Africa, reflecting regional disruptions. However, the IMF expects a rebound in these regions in 2026 as disruptions ease and economic stability returns.
Conclusion
The IMF’s latest global growth forecast for 2025 underscores the ongoing challenges faced by economies worldwide, particularly as trade tensions continue to disrupt global supply chains. With lower growth projections for major economies like the US, China, and Europe, as well as increasing financial risks, the global economic landscape remains uncertain. As the IMF continues to monitor these developments, the impact of tariffs and trade policies will undoubtedly shape the global economy in the years to come.
The IMF’s revision highlights the need for strategic international cooperation and policy adjustments to navigate these turbulent economic times.




